How to do bean injection in spring-boot
Archive for the ‘ Spring Boot ’ Category
LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
Listen 9030 SSLProxyEngine On SSLProxyVerify none SSLProxyCheckPeerCN off SSLProxyCheckPeerName off SSLProxyCheckPeerExpire off RequestHeader set Front-End-Https "On" #NameVirtualHost * <VirtualHost localhost:9030> <Proxy https://localhost:7147/*> Allow from all </Proxy> <LocationMatch "/test-rest"> ProxyPass http://localhost:7147/test-rest ProxyPassReverse http://localhost:7147/test-rest Header add REMOTE_VALUE "2" RequestHeader set REMOTE_VALUE "2" </LocationMatch> </VirtualHost>
Project used:
simple-rest-which-accepts-header
– Download and extract from http://www.jasypt.org/download.html
– Run the below from the bin of the extracted download:
encrypt.bat input="testuser" password=MY_PASS
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId>
<artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.14</version>
</dependency>
– Place the generated text between “ENC(” and “)”
– Build the project.
– Run the below from project directory:
mvn spring-boot:run -Djasypt.encryptor.password=MY_PASS
– Run the below from project target directory:
java -jar target\jasypt-test-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --jasypt.encryptor.password=MY_PASS
1. Create project from “Spring initialz” with 3 dependencies:
a. Web
b. Actuator (Optional)
2. A REST Controller.
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/employee")
public @ResponseBody Map<String, String> getEmployee(@RequestBody JsonNode jsonNode){
String name = jsonNode.get("name").asText();
System.err.println("[Calling][getEmployee][name]"+name);
Map<String, String> namefEmployee = new HashMap<>();
namefEmployee.put("Name of Employee", name);
return namefEmployee;
}
}
3. Run mvn spring-boot:run to start the service.
4. Testing with Postman client.
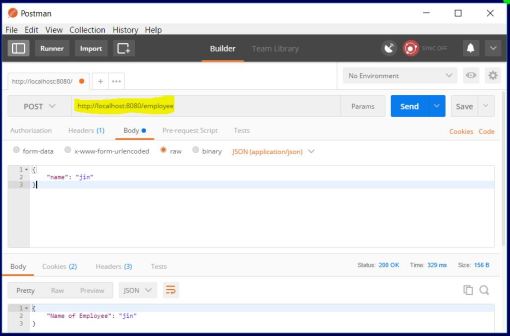
1. Create project from “Spring initialz” with 3 dependencies:
a. Web
b. Actuator (Optional)
2. Additional maven dependencies.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
see full pom.xml
3. RestTemplate sample usage
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
public class SpringRestClient {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public SpringRestClient() {
ClientHttpRequestFactory requestFactory = getClientHttpRequestFactory();
this.restTemplate = new RestTemplate(requestFactory);
restTemplate.getMessageConverters().add(new StringHttpMessageConverter());
}
public void sendRequest2() throws URISyntaxException {
String requestJsonString = "{ \"name\": \"user1\"}";
String requestUrl = "http://localhost:8080/employee";
// set headers
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<String> entity = new HttpEntity<String>(requestJsonString, headers);
// send request and parse result
ResponseEntity<String> restResponse = restTemplate
.exchange(requestUrl, HttpMethod.POST, entity, String.class);
System.err.println("response string: " + restResponse.getBody());
}
private ClientHttpRequestFactory getClientHttpRequestFactory() {
int timeout = 60000;
RequestConfig config = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(timeout)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(timeout)
.setSocketTimeout(timeout)
.build();
CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder
.create()
.setDefaultRequestConfig(config)
.build();
return new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(client);
}
}
3. Run mvn spring-boot:run to test the project.
<build>
...
<plugins>
...
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<classifier>exec</classifier>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
...
</build>
Sample usage:
Code sample:
spring-boot-as-dependency
1. Create project from “Spring initialz” with 3 dependencies:
a. Web
b. Security
c. Actuator (Optional)
2. The sample service to get user from database/data store:
@Service
public class UserService {
Map<String, String> mapUserWthId = new HashMap();
public UserService() {
mapUserWthId.put("a1", "A");
mapUserWthId.put("a2", "B");
mapUserWthId.put("a3", "C");
mapUserWthId.put("a4", "D");
}
/**
* Assuming that this will fetch from a database .
*/
public String getUserNameByID(String userId) {
return mapUserWthId.get(userId);
}
}
3. The authentication provider (Check reference for details):
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(CustomAuthenticationProvider.class.getName());
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
String name = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
// Should check with database or some services for authentication
if (userService.getUserNameByID(name) != null) {
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, "User [{0}] authorize!", name);
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
name, password, new ArrayList<>());
} else {
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, "User [{0}] not authorize!", name);
return null;
}
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return authentication.equals(
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
4. The security configuration:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationProvider authProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().httpBasic();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authProvider);
}
}
5. The Rest controller:
@RestController
public class GreetingController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/greetings/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String getGreetingMessage(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return "Hello user: "+ name;
}
}
6. Testing by navigating to the blow:
http://localhost:8080/greetings/greenhorn
7. End
| Source Code: The sample spring boot maven project used for this exercise can be downloaded from: |
|---|
a. liquibase
b. mysql
c. jpa
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/liquibase_test
username: greenhorn
password: greenhorn
liquibase:
check-change-log-location: true
enabled: true
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<databaseChangeLog xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog" xmlns:ext="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog-ext" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog-ext http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-ext.xsd http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-3.5.xsd">
<changeSet author="generated" id="tbl-1">
<createTable tableName="test_tbl">
<column name="tblId" type="VARBINARY(36)">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="createdDate" type="datetime">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="updatedDate" type="datetime"/>
<column name="fk_createdBy" type="VARBINARY(36)">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="fk_updatedBy" type="VARBINARY(36)"/>
<column name="active" type="BIT(1)"/>
<column name="deleted" type="BIT(1)"/>
<column name="content" type="VARCHAR(255)">
<constraints nullable="false"/>
</column>
<column name="version" type="INT"/>
</createTable>
</changeSet>
<changeSet author="generated" id="tbl-2">
<addPrimaryKey columnNames="tblId" constraintName="PRIMARY" tableName="test_tbl"/>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>
@Configuration
public class LiquibaseConfig {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Bean
public SpringLiquibase liquibase() throws Exception {
// Locate change log file
String changelogFile = "classpath:db/mysql/changelog/db.changelog-test.xml";
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(changelogFile);
Assert.state(resource.exists(), "Unable to find file: " + resource.getFilename());
// Configure Liquibase
SpringLiquibase liquibase = new SpringLiquibase();
liquibase.setChangeLog(changelogFile);
liquibase.setDataSource(dataSource);
liquibase.setDropFirst(true);
liquibase.setShouldRun(true);
// Verbose logging
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("verbose", "true");
return liquibase;
}
}
| NOTE The sample spring boot maven project used for this exercise can be downloaded from: |
|---|